Our analysis of just under 1.8 million papers with abstract information in arXiv, bioRxiv and medRxiv reveals 82,423 artificial intelligence (AI) papers (4.6 per cent of the total), 5,450 COVID-19 papers (0.3 per cent of the total) and 379 AI papers that focus on COVID-19 (0.21 per cent of the total).
In order to study the representation of AI in COVID-19 research, we subset the data to focus on 2020 when 98.7 per cent of the COVID-19 papers in our data were published and compare the share of AI papers in non-COVID-19 research with their share outside COVID-19 research.
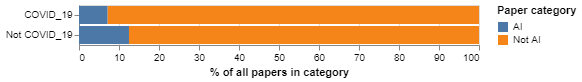
As Figure 1 shows, research relating to COVID-19 is less likely to deploy AI techniques than research outside this topic. Just 7.12 per cent of papers about COVID-19 mention AI, whilst for papers that are not about the pandemic the figure increases to 12.49 per cent. The presence of AI research in COVID-19 is 43 per cent lower than we would expect if AI was present there at the same frequency as in other topics.
Figure 1: The share of AI research inside COVID-19 is lower than the share outside
An interactive version of this graph is available in the online report
When we consider various trends of interest in Figure 2, we find that the share of COVID-19 activity in our corpus has been growing rapidly to reach around 10 per cent of all research in our corpus, highlighting the velocity with which the scientific community has reoriented its efforts to tackle COVID-19, and the importance of preprints as an outlet to disseminate their efforts. COVID-oriented AI research has also grown since around March 2020, although it has stabilised now at around 6 per cent of all of all AI research. Interestingly, the share of AI research in papers about COVID-19 research is stagnant or even declining after a peak of activity towards the end of March 2020.
Figure 2: COVID-19 research is gaining importance but the share of AI in it is stable or even stagnant
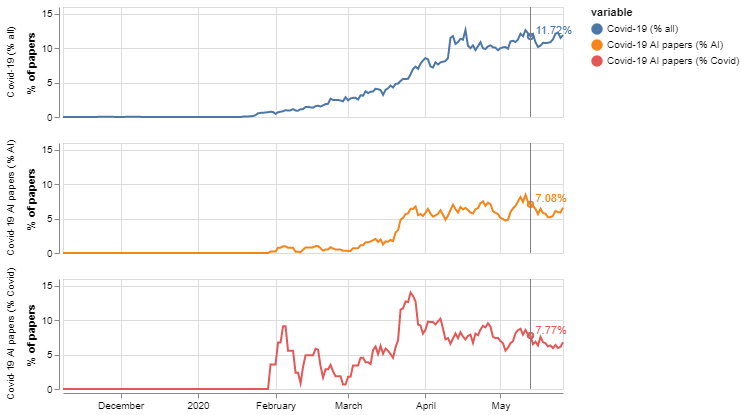
Figure 2: COVID-19 research is gaining importance but the share of AI in it is stable or even stagnant
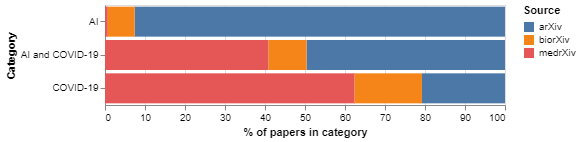
We also consider the share of papers in categories of interest accounted for by different article sources (arXiv, bioRxiv and medRxiv). As Figure 3 shows, arXiv accounts for more than 90 per cent of AI papers in our corpus but only 20 per cent of the COVID-19 papers. When we look at the intersection between both categories, we find that arXiv accounts for half of the AI papers to tackle COVID-19, and medrXiv and biorXiv for the rest. This is consistent with the idea that researchers from various disciplines are exploring ways to deploy AI research in order to tackle COVID-19, and justifies our decision to incorporate arXiv into the analysis.
Figure 3: Share of relevant categories accounted by different sources
An interactive version of this graph is available in the online report






